Essential Guide to How to Do Synthetic Division: Master the Process in 2025
Essential Guide to How to Do Synthetic Division
What is Synthetic Division?
Synthetic division is a shortcut method for performing polynomial division, especially useful when dividing by linear binomials of the form (x – c). This process simplifies the division of polynomials significantly, allowing students and professionals alike to efficiently find the quotient and remainder. Considered a fundamental technique in algebraic operations, synthetic division capitalizes on the coefficients of the polynomial rather than dealing directly with the polynomial expressions themselves. Through this guide, you will master synthetic division by understanding its rules, applications, and step-by-step methodology.
Understanding the Synthetic Division Method
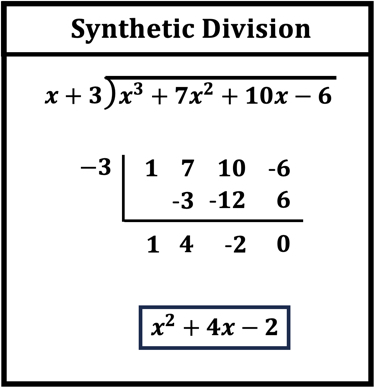
The synthetic division method begins with setting up a division space where you write down the numerical coefficients of the polynomial in descending order of the degree of the polynomial. For example, for the polynomial 2x3 + 3x2 – 4x + 5, the coefficients would be (2, 3, -4, 5). By substituting the value of c from (x – c), you can bring down the leading coefficient to start your synthetic division process. Follow through the synthetic division steps to derive the quotient whilst addressing the remainder at each stage. This efficient process eliminates the heavy computations found in traditional long division.
Key Steps in Performing Synthetic Division
To perform synthetic division, follow these systematic steps:
- Write down the coefficients of the polynomial you are dividing.
- Write the value of c from your divisor on the left.
- Bring down the leading coefficient on the right.
- Multiply c by the number just brought down and place the result under the next coefficient.
- Add the numbers in the second column to find the next coefficient.
- Repeat the multiplication and addition process until all coefficients are processed.
This structured approach gives clarity and helps avoid common mistakes when dividing polynomials, making your results more reliable and easier to double-check.
Tools to Enhance Understanding of Synthetic Division
Learning resources such as synthetic division calculators and online tutorials offer assistance in mastering this technique. Many platforms provide synthetic division exercises tailored to different learning levels. You can also find numerous instructional videos that walk you through example problems in real-time. Engaging with these educational tools not only helps solidify your understanding but also encourages hands-on practice with immediate feedback to check answers. Implementing these resources can streamline your learning path and clarify any misconceptions surrounding synthetic division.
Applications of Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is widely applicable, particularly when evaluating polynomial equations or finding roots of polynomial functions. It provides an efficient mechanism not only for evaluating functions but also for analyzing polynomial graphs for zeroes and factors. This tool is invaluable in fields like algebra, calculus, and various mathematical proofs where polynomial manipulation is often required.
Polynomial Relationships and Divisor Usage
A critical application of synthetic division is the identification of polynomial relationships through the remainder theorem. When using this theorem, if a polynomial f(x) is divided by (x – c), the remainder of that division is simply f(c). This creates a bridge between polynomial evaluation and division, enhancing understanding of functions at a high level. Understanding how to manipulate these relationships can vastly improve performance in polynomial-related problems.
Examples of Synthetic Division in Action
To exemplify, suppose we wish to conduct synthetic division on f(x) = 2x3 + 3x2 – 4x + 5 by (x – 1). Setting c = 1, we would set up our synthetic division space as follows:
- Coefficients: 2, 3, -4, 5
- Setup value c = 1
Following the steps outlined earlier, you would find that the resulting polynomial from this operation is 2x2 + 5x + 1 with a remainder of 6. Such examples confirm the process and establish practice in executing synthetic division successfully.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When engaging with synthetic division, it’s vital to be cautionary about potential pitfalls. Common mistakes include errors in aligning coefficients or miscalculating during the multiplication phase. Review your steps and utilize a synthetic division worksheet before venturing into more complex problems. Additionally, the use of interactive lessons can enhance understanding and retention by providing live feedback through synthetic division hints.
Checking Your Answers
One robust technique to ensure accuracy in synthetic division is to check your answers using the long division method. While more extensive, comparing results from both methods can provide a reliable verification process. Furthermore, using a synthetic division calculator online offers instant feedback and highlights mistakes which can be further analyzed and rectified.
Additional Resources to Aid Learning
Students looking to deepen their comprehension can explore resources available online that focus on hands-on practice, such as interactive modules and synthetic division worksheets. These platforms also often contain example problems and visual aids that enhance understanding by illustrating the connection between numerical coefficients and the outputs of polynomial functions.
Key Takeaways
- Synthetic division is an efficient method for dividing polynomials, especially by linear binomials.
- Understanding the structure and rules of synthetic division is crucial to mastering the process.
- Utilizing available educational tools and exercises can significantly improve your grasp of synthetic division.
- Practical examples and careful checks can enhance your accuracy and confidence in using this process.
- Engaging with common resources can prepare you for polynomial equations in advanced math contexts.
FAQ
1. What is the main advantage of using synthetic division over long division?
The primary advantage of using synthetic division is its efficiency. It simplifies the calculations by focusing solely on the coefficients of the polynomial, thus speeding up the process significantly compared to traditional long division. This is especially beneficial when dealing with higher-degree polynomials.
2. Can synthetic division be used for polynomials with fractional coefficients?
Yes, synthetic division can also be applied to polynomials with fractional coefficients. The procedure remains the same; ensure proper handling of fractions during multiplication and addition to maintain accuracy.
3. How can I practice synthetic division effectively?
Effective practice of synthetic division can be achieved through online tutorials, worksheets, and engaging in hands-on practice. Many educational websites provide structured exercises that cater to various difficulty levels.
4. What is the connection between synthetic division and the Remainder Theorem?
The Remainder Theorem states that the remainder of the division of a polynomial f(x) by a linear divisor of the form (x – c) is simply f(c). This is directly applicable in synthetic division—where the result includes both the quotient and the remainder efficiently derived.
5. Are there any common mistakes to be aware of in synthetic division?
Common mistakes in synthetic division include errors in copying coefficients, misaligned steps, or incorrect multiplication results. Practicing with synthentic division examples can help identify and resolve these issues effectively.
6. How does synthetic division help in evaluating polynomials?
Synthetic division aids in evaluating polynomials by allowing for quick calculations at specific values. It is particularly useful for finding zeros of polynomial functions, as it provides a direct path to determine if a function has roots at designated points.
7. What resources are best for understanding synthetic division?
Recommended resources include educational websites that offer interactive lessons, guided exercises, and synthetic division calculators. These tools often provide detailed explanations and step-by-step solutions which enhance understanding.