How to Properly Update Windows 10 Drivers for Optimal Performance in 2025
How to Properly Update Drivers for Windows 10 for Optimal Performance in 2025
Keeping your Windows 10 system running smoothly in 2025 requires an understanding of how to update drivers. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about updating drivers, utilizing tools, and troubleshooting any potential driver issues. Ensuring your drivers are up-to-date will improve system performance, enhance security, and support new devices effectively.
Understanding Driver Updates
Driver updates are essential for maintaining robustness and compatibility with new hardware and software. **Device drivers** enable Windows 10 to communicate effectively with your hardware components, like graphics cards, network adapters, and audio devices. By routinely performing **driver updates**, you can resolve compatibility issues and enhance system performance. Furthermore, outdated drivers can lead to frequent crashes or degraded performance. For the best results, it’s critical to identity whether you need **manual driver installation** or if an **automatic driver update** would suffice. Windows Update can sometimes handle this process for you, streamlining the effort required to keep your system optimized.
The Importance of Updating Device Drivers
Regularly updating your **device drivers** corresponds to several benefits. First and foremost, updates often come with fixes for bugs that could be causing crashes or poor performance. **Driver incompatibility** can result in diminished hardware capability, leading to frustrating performance issues. Additionally, driver updates often include performance enhancements, allowing your hardware, such as your **graphics driver**, to take full advantage of system capabilities. Consequently, ensuring your drivers are current is crucial for an optimized computing experience.
When to Update Your Drivers
Recognizing the right time to update your **drivers** can save time and improve system functionality. It’s generally advisable to check for updates after significant software installations, during Windows updates, or prior to installing new hardware. Additionally, if you encounter specific **driver issues**, such as audio malfunctions or unstable graphics, updating the corresponding **device driver** is usually a straightforward solution. Always keep an eye on updates from your device manufacturer’s website for the **latest drivers**, as these might not be included in Windows Update.
Driver Management Tools for Windows 10
Windows 10 provides a built-in **Device Manager**, which allows users to **search for drivers** or **install drivers** manually when necessary. Navigating to Device Manager enables you to view and manage all connected devices efficiently. If you insert new hardware, Device Manager helps identify if the **driver software** is correctly installed or if the program needs troubleshooting. For users desiring more enhanced functionality, a range of **best driver update tools** exists, offering easy and effortless ways to automate the update process.
Methods to Update Drivers
There are two principal methods for updating drivers on Windows 10: using Device Manager and relying on **Windows Update**. Depending on your needs, you can opt for either approach. Each method has its merits and could potentially save you a considerable amount of time and hassle during the update process. Knowing how to navigate through both methods is key to effective driver management and ensuring high system performance.
Using Device Manager for Updates
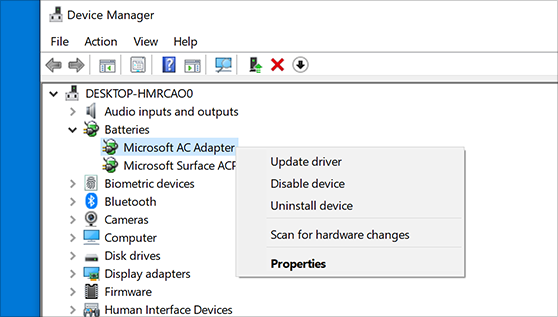
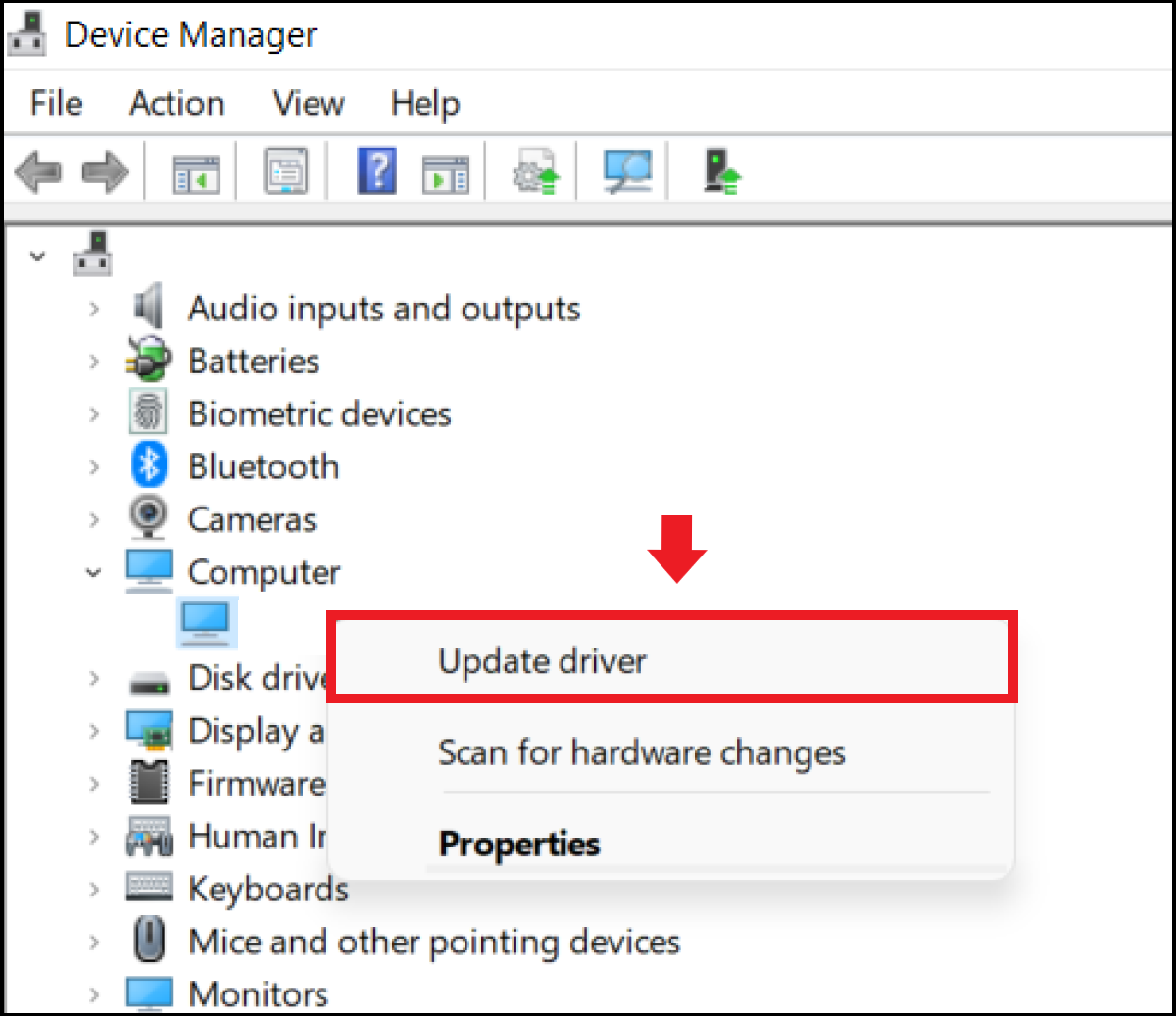
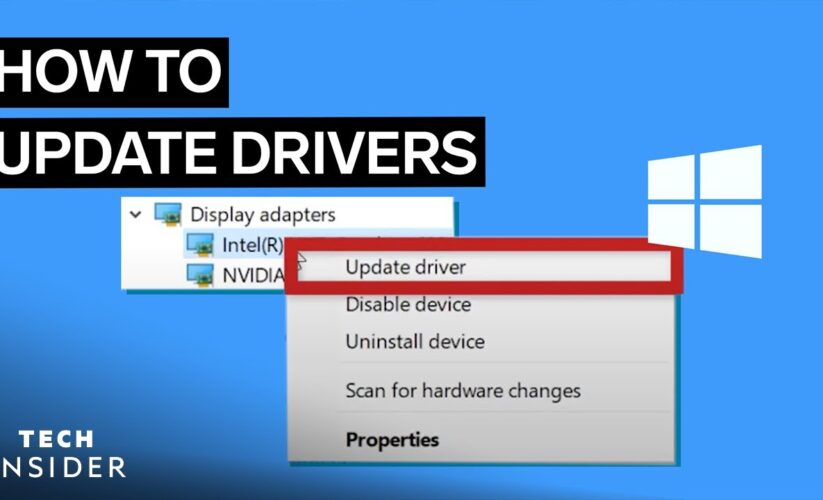
Device Manager serves as a comprehensive interface to manage your hardware devices efficiently. To use Device Manager for **driver updates**, simply open the application, find the device that requires an update, and right-click to select “**Update Driver Software**.” At this point, you can choose to search automatically for **updated drivers** or to point to a specific location where you have the necessary **driver installation files**. This targeted approach is best for ensuring the accuracy and compatibility of the new drivers.
Performing Windows Update for Driver Installation
Windows Update is another efficient method to keep your system current. It not only automates the search for compatible driver updates but also streams various software updates vital for overall system health. To check for updates, navigate through “Settings” > “Update & Security” > “Windows Update” and click “Check for updates.” If any new **driver software updates** are available, Windows will prompt you to install them. Monitoring Windows Update guarantees that you’ll receive all **hardware drivers** updated for better system integration and stability.
Optimizing Your Driver Installation
When performing updates—whether through **manual driver installations** or **automatic updates**—it is fundamental to optimize your process. This includes regularly performing backups before installations, ensuring to have some knowledge of system **driver compatibility**, and checking for updates frequently. Create a system restore point before major installations or obtain a **driver backup** to simplify rollback in case of conflicts post-update, ensuring a secure system management experience.
Troubleshooting Driver Issues
Despite your best efforts to maintain your drivers, problems may occasionally arise. Issues could stem from newly installed drivers that cause compatibility problems or lead to system instability. Understanding how to effectively troubleshoot is essential to keeping smooth performance and resolving potential crashes. Through diligent troubleshooting techniques, users can quickly identify and correct issues related to **driver problems**.
Common Driver Problems and Solutions
Common issues include screen freezes associated with outdated graphics drivers, missed network connections due to a faulty **network adapter driver**, or sound malfunctions arising from an outdated **audio driver update**. To resolve these problems, identify the specific issue, find the improper driver through Device Manager, and opt to either update or uninstall it, enabling a seamless reinstallation of updated drivers. Monitoring forums and developer logs can also provide additional insights into frequently faced challenges within the driver ecosystem.
Utilizing Driver Troubleshooting Tools
If manual approaches to resolve driver issues are proving ineffective, consider the utility of automatic **driver troubleshooting** tools. These tools integrate with Windows 10 and help diagnose, identify, and resolve driver-related conflicts thoroughly. By systematically processing standard checks, these tools bridge communication between user inputs and comprehensive support for **finding hardware drivers** and resolving complex compatibility issues with a user-friendly interface.
Restoring Previous Driver Versions
If an update has detrimental effects on your system, you can roll back to a previously installed version of a driver via Device Manager. Right-click the target device, select “Properties,” navigate to the “Driver” tab, and click “Roll Back Driver.” This option reverts your driver to the last known functional iteration, which often helps alleviate performance concerns. Always ensure you maintain those older drivers safely when updating to regain stability quickly if new updates lead to issues.
Key Takeaways
- **Regular driver updates** are essential for maintaining system compatibility and performance.
- Utilizing **Device Manager** and **Windows Update** can significantly simplify the update process.
- Establish a routine for checking drivers, especially after major updates or installations.
- Effective troubleshooting and driver rollback plans can resolve most related issues.
- Driver backup and integrity checks are crucial for maintaining optimal system performance.
FAQ
1. How often should I check for driver updates?
It is advisable to check for driver updates at least once every month. Additionally, always check after installing new software or hardware. Regular **driver updates** help ensure system stability and performance.
2. What tools can assist with driver installation?
Several **best driver update tools** exist that can automate the process of **installing drivers**. Consider options like Driver Booster and SnailDriver, which efficiently manage updates and can detect old or **outdated drivers** quickly.
3. How do I back up my drivers?
You can back up drivers using software like DriverBackup! or the built-in Backup facility in OTG programs. This process safeguards against data loss during major system changes or crashes, making it easy to restore drivers when necessary.
4. What should I do if my device stops functioning after a driver update?
In this case, try rolling back to the previous driver version via Device Manager. Go to the device properties and use the “Roll Back Driver” function. If issues persist, uninstall the drivers and reinstall the correct ones.
5. Are there security risks associated with outdated drivers?
Yes, outdated drivers can expose your system to vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit. Regular updates are essential to minimize security risks, enhancing your system’s overall defense against malware and unauthorized access.
6. How can I tell if my drivers are outdated?
You can check device performance issues in Device Manager or look for announcements from your hardware manufacturer about new versions. Tools like Driver Booster can also scan your system for **driver compatibility** and prompt updates quickly.
7. What are the signs of driver mismanagement?
Typical symptoms of driver mismanagement include frequent crashes, poor device performance, glitches in graphical output, or unresponsive hardware. Maintaining an organized approach to updates and utilizing necessary tools can mitigate these problems.
For more insights on effectively managing and updating your drivers, check our guides at this link and this one.