How to Properly Find the Expected Value: A Complete Guide for 2025
“`html
How to Properly Find the Expected Value: A Complete Guide for 2025
Understanding the concept of expected value is crucial for anyone involved in probability and decision-making processes. The expected value formula allows us to synthesize potential outcomes to inform better choices in various fields, including finance, statistics, and game theory. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different aspects of expected value, including its calculation, properties, and applications in real-life scenarios.
Understanding the Expected Value in Statistics
The expected value in statistics serves as a fundamental concept that quantifies the average outcome of random variables. When dealing with a discrete random variable, the expected value can be computed by summing the products of each outcome’s value and its associated probability. This approach helps in forming a clear understanding of what one might expect when making decisions based on uncertain outcomes.
Definition of Expected Value
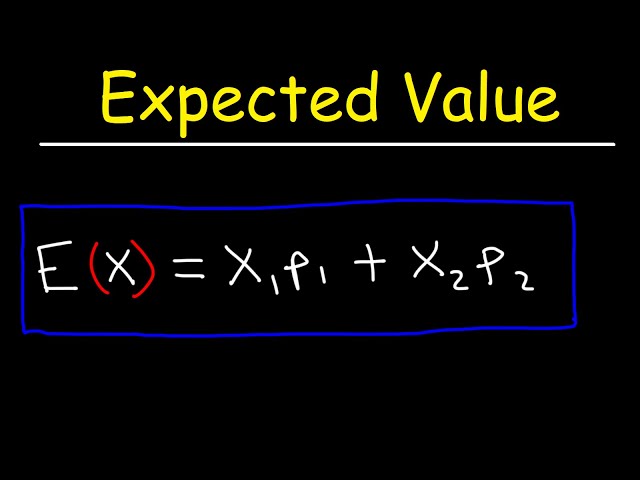
The definition of expected value is straightforward: it is the weighted average of all possible values that a random variable can take, with weights being the probabilities of each outcome. This foundational concept is essential for grasping how to find expected value and applying it effectively in real-world scenarios such as economics and finance. Mathematically, we express this as:
E(X) = Σ [x * P(x)]
where E(X) is the expected value, x represents each outcome, and P(x) denotes the probability of that outcome.
Mathematical Expectation Explained
Often referred to simply as mathematical expectation, expected value provides insight into the average result one can anticipate from a probability distribution. This is crucial, especially in fields such as economics and finance, where it helps in assessing risk and making investment decisions. For instance, if you want to calculate the expected value of a random variable that can take on multiple outcomes based on market conditions, applying the expected value formula assists in evaluating potential gains versus risks.
Properties of Expected Value
The properties of expected value are pivotal in understanding its implications in statistics. One property worth noting is the linearity of expectation, which states that the expected value of a sum of random variables is equal to the sum of their expected values, regardless of whether the variables are independent. This property highlights how the expected value can simplify calculations in complex situations and decision-making models.
Calculating Expected Value
Now that we have a foundational understanding of expected value, let’s delve into how to find expected value effectively. Follow these outlined steps, and you’ll become proficient in calculating expected value for various scenarios.
Finding Expected Value of Discrete Random Variables
To find the expected value of discrete random variables, you can follow these steps:
1. **Identify all possible outcomes (x)** of the random variable.
2. **Determine the probability (P)** for each outcome.
3. **Multiply each outcome by its probability** to find the weighted value.
4. **Sum these weighted values** to get the expected value.
For example, consider a simple dice roll. The probability of each face (1-6) is \( \frac{1}{6} \). So, the expected value would be:
E(X) = Σ [x * P(x)] = (1+2+3+4+5+6) * (1/6) = 3.5
This means that if you roll the die many times, the average result will be approximately 3.5.
Expected Value of a Function
When the random variable is a function of other variables, expected value of a function applies. You simply need to calculate the value of the function at each outcome and follow the same summation procedure for the probabilities. For instance, if f(x) = x^2 and you want to calculate its expected value over outcomes of a die roll, you would find:
**E(f(X)) = Σ [f(x) * P(x)] = E(x^2) = (1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + 4^2 + 5^2 + 6^2) * (1/6) = 15.5.**
Applications of Expected Value in Decision Making
The applications of expected value are vast, especially in decision-making. Whether you’re assessing risk in investments, analyzing betting strategies, or evaluating potential outcomes in business scenarios, understanding expected value helps clarify complex choices. For example, in marketing analysis, utilizing expected value can guide strategies by predicting the average return from multiple campaigns, helping businesses optimize their operations.
Expected Value vs Variance
Understanding expected value vs variance is essential in risk assessment and making informed decisions. While expected value predicts the average outcome, variance measures the spread or risk associated with that outcome. In financial contexts, balancing expected value with variance allows investors to understand not just potential profits but also the risks attached to various investments. For example, an investment with a high expected value but even higher variance may indicate a potentially risky scenario.
Calculating Variance in Relation to Expected Value
Often, it’s beneficial to calculate variance in addition to expected value to gain insight into data spread. Variance can be calculated using the formula:
Var(X) = E(X²) – (E(X))²
This will give a clear picture of the variability of the outcomes around the expected value, indicating potential risk levels. For instance, if the expected value of an investment is high, but the variance is equally high, it could give indications that other risk factors might need to be considered before making a decision.
Expected Value in Finance and Investment Decisions
In finance, the expected value for investment plays a critical role in portfolio management and strategic planning. By evaluating the expected return on investments using past performance data, investors can make calculated risk decisions; quantifying both expected values and variances provides a more complete risk assessment framework. This helps investors gauge potential losses vs. gains, thus facilitating informed portfolio adjustments.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the expected value is crucial for making informed decisions in uncertain situations.
- Calculating expected values involves identifying outcomes and their probabilities, then applying the expected value formula.
- Expected value application spans across finance, economics, game theory, and probability, informing strategies and risk assessments.
- Comparing expected value with variance enhances risk evaluation, allowing better decision-making in finance and business.
- Utilizing expected value in marketing and everyday scenarios contributes to optimizing outcomes and maximizing success.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of expected value in decision making?
Expected value acts as a guiding principle in decision making by providing a calculated average of potential outcomes weighted by their probabilities. This allows individuals and businesses to make informed choices by assessing which scenarios might yield the highest benefits over time, thus helping to simplify complex risks and choices.
2. How does expected value relate to probability distributions?
Expected value is derived from probability distributions, which outline all possible outcomes and their probabilities. It represents a measure of the center of the distribution, effectively summarizing what one can expect in the long term when outcomes repeat, making it a central concept in statistical analysis.
3. Can expected value be applied in insurance?
Yes, in insurance, the concept of expected value is extremely relevant as it helps in pricing premiums. Insurance companies analyze the expected outcomes of loss scenarios and set premiums accordingly to assure that the expected returns align strategically against risk—each policy designed around calculated expected values ensures profitability.
4. What are examples of expected value in gambling?
In gambling scenarios, expected value examples in gambling can illustrate how players can determine whether a game offers a net profit or loss over time. By analyzing game rules, payout odds, and probabilities of winning, gamblers use expected value to shape their betting strategies, making it vital in understanding outcomes in games of chance.
5. How does expected value factor in game theory?
In game theory, expected value in game theory helps predict outcomes based on the strategies applied by players. Understanding expected value enhances strategic planning and assessment of risks, allowing players to determine the best actions based on their chances of achieving favorable outcomes.
“`