How to Calculate Percent Yield: Essential Guide for Chemistry Success in 2025
“`html
How to Calculate Percent Yield: Essential Guide for Chemistry Success in 2025
Understanding how to calculate percent yield is a vital skill for chemists, whether in academic labs or industrial settings. This guide will walk you through the intricacies of yield calculation, helping to enhance your knowledge and improve experimental results. By grasping the concepts behind actual yield and theoretical yield, you’ll position yourself for success in chemistry. We’ll explore essential lab techniques, discuss optimization strategies, and provide practical examples to improve your yield data. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Percent Yield
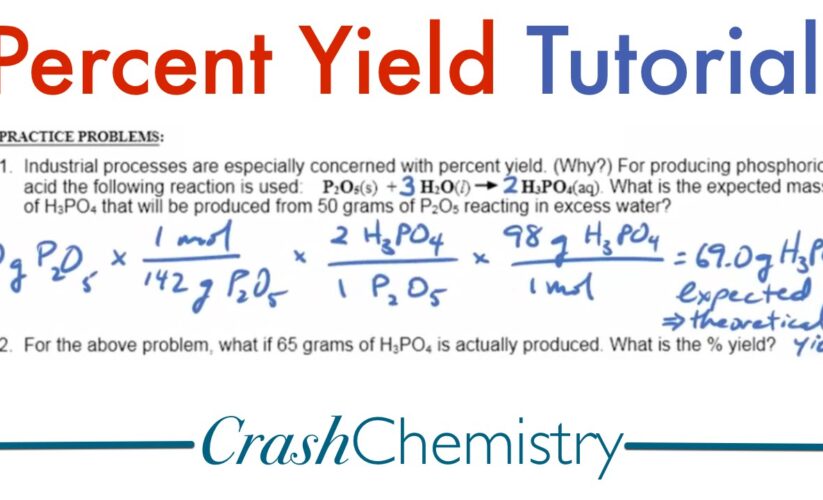
To commence, it’s necessary to define percent yield. The percent yield is a critical measure that compares the actual yield obtained from a chemical reaction to the theoretical yield expected, expressed as a percentage. This measurement indicates the efficiency of a reaction. For instance, if 10 grams of product are anticipated (theoretical yield) and only 8 grams are obtained (actual yield), the percent yield can be calculated using the formula:
Percent Yield = (Actual Yield / Theoretical Yield) x 100%.
Percent Yield Definition and Importance
The definition of percent yield serves as a foundation for assessing the success of a chemical reaction. While a high percent yield signifies a more efficient process, a low rate can indicate problems within the reaction, such as incomplete reactions, loss of product during recovery, or measurement inaccuracies. Understanding these yield factors can help chemists make informed adjustments to improve reaction efficiency. Before diving into calculations, one should familiarize themselves with basic concepts, such as stoichiometry and the underlying principles of each reaction involved.
Yield Calculation Steps
Calculating percent yield involves several key steps. First, you will need to determine the amounts of reactants utilized and their expected conversion rates to products. Here’s a simple step-by-step approach:
- Write the balanced chemical equation.
- Calculate the theoretical yield from stoichiometric relationships.
- Measure the actual yield of the product after the reaction has occurred.
- Substitute these values into the percent yield equation.
This systematic method will ensure accurate and reliable yield calculations, paving the way to optimization.
Factors Affecting Yield
There are several yield factors influencing the results of your experiment, including reaction conditions like temperature, reaction time, and purity of reactants. Understanding these factors is crucial for maximizing reaction progress and achieving a better product yield in chemistry. For example, in a synthetic reaction, if the temperature is insufficient, it might slow down reaction kinetics, thereby reducing the actual yield. By carefully analyzing these parameters, chemists can identify opportunities for improvement.
Yield Improvement Techniques
Improving yield is often a matter of fine-tuning your processes in practical chemistry. Different yield improvement techniques can lead to substantial enhancements in chemical yield. Here are some strategies to consider:
Optimizing Reaction Conditions
One of the main strategies for enhancing percent yield is optimizing reaction conditions. This could involve adjusting temperature and pressure, changing solvents, or reorganizing reactant ratios to find the best fit for the chemical reaction underway. Careful trial and error, guided by the principles of stoichiometry, will enable you to map out the best conditions for optimal yield.
Utilizing Advanced Analytical Techniques
Employing advanced analytical techniques early in the experimentation phase can also reveal insights into chemical interactions, offering avenues for refined yield analysis. Technologies like gas chromatography (GC) or liquid chromatography (LC) allow chemists to monitor reaction kinetics closely and adjust the process in real-time to ensure better product yield and minimize waste.
Test and Document Yield Data
Documentation of every experiment’s yield data provides a wealth of information for future reference. By analyzing past processes’ results, chemists can identify patterns and predict possible deviations or improvements in new experiments. Implementing excellent laboratory practices will ensure high-quality yield reporting and set a robust foundation for ongoing research.
Practical Applications in Academic Labs
In academic settings, understanding and improving percent yield is crucial for students involved in chemistry and other related disciplines. The integration of quantitative analysis and conceptual learning aids the mastery of yield calculation examples in a practical context. Here’s how:
Academic Perspectives on Yield
Evaluation of data across multiple experiments in academic environments enhances the learning experience for aspiring chemists. By engaging in repeated trial-and-error revisions and experiments, students can experience firsthand the influence of various yield factors and how they align with classroom theory. This bridging between practical labs and theoretical principles fosters critical thinking skills.
Yield Comparison During Experimentation
When students document their yield calculations, they can compare their results and identify discrepancies between expected and actual yields. Through discussions and investigations of these variations, trends can emerge, shedding light on real-world chemical methodologies and fostering deeper contextual understanding.
Assessing Yield Variability
Students in academic labs should be encouraged to assess yield variability over consecutive lab assignments. Continuous monitoring helps foster an environment of improvement and open-minded experimentation, boosting their problem-solving and analytical competencies alongside their understanding of chemical processes.
Key Takeaways
- The percent yield measures the efficiency of a chemical reaction, comparing actual and theoretical values.
- Optimizing reaction conditions, such as temperature and the purity of reactants, can increase chemical yield.
- Implementing advanced analytical techniques can aid in understanding reaction dynamics.
- Documentation and graduated comparisons in laboratory settings enhance learning opportunities.
FAQ
1. What is the significance of percent yield in chemical experiments?
The significance of percent yield lies in its ability to assess the effectiveness of chemical reactions. It informs scientists about how well reactants convert into products, guiding adjustments for improved experimental designs.
2. How does one calculate theoretical yield?
Theoretical yield is calculated by using stoichiometric coefficients from a balanced equation, allowing you to determine the maximum possible product from given reactant amounts. It serves as a cornerstone for the yield calculations.
3. What factors can lead to low yield in an experiment?
Several factors can contribute to low yield, including incomplete reactions, loss of product during purification, or inaccurate measurements. Identifying these issues often involves a thorough review of the reaction settings.
4. How can yield be improved in laboratory processes?
Yield improvement can be achieved by refining reaction conditions, implementing effective purification techniques, and adopting real-time monitoring technologies. Regular yield analysis and optimizations can lead to better outcomes.
5. What role does stoichiometry play in yield calculations?
Stoichiometry is fundamental for determining theoretical yield, as it provides the relationship between reactants and products in a given chemical reaction. Understanding these relationships is key for accurate yield calculations and improvements.
“`