How to Effectively Find Marginal Cost in 2025 for Your Business
How to Effectively Find Marginal Cost in 2025 for Your Business
Understanding marginal cost is crucial for making informed financial decisions in your business. It reflects the change in total cost that arises when the quantity produced is incremented by one additional unit. In 2025, with advancements in technology and analytics, calculating marginal cost can be done more effectively than ever. This article explores the definition of marginal cost, how to calculate marginal cost, its implications for business economics, and how you can integrate this principle into your operational strategy.
Understanding Marginal Cost
The marginal cost formula is the backbone of decision-making in cost concepts in economics. It is defined as the change in total cost that occurs when one additional unit of a good or service is produced. The combined impact of fixed costs versus marginal costs is critical in determining the total cost structure of production. Understanding this economic theory helps businesses optimize their production levels and pricing strategies.
Definition of Marginal Cost
The definition of marginal cost revolves around its role in production cost analysis. Marginal cost exists where the total cost fluctuates as output changes. This concept separates costs into variable costs and fixed costs, enabling businesses to differentiate between what expenses are incurred through additional production. A clear grasp of this definition sets the standard for more complex applications like marginal cost pricing and will guide effective managerial economics decision-making.
Calculating Marginal Cost
To calculate marginal cost, one must first identify both total costs before and after producing an additional unit. The formula is: Marginal Cost (MC) = Change in Total Cost / Change in Quantity. For instance, if the total cost of producing 100 units is $1,000, and then it increases to $1,050 for 101 units, the marginal cost for that additional unit is $50. This calculation assists in determining how production decisions can pivot based on costs.
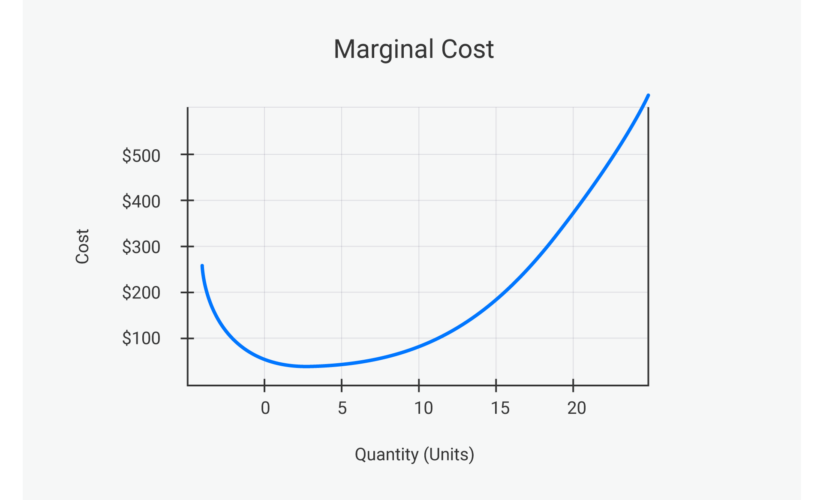
Marginal Cost Curve
The creation of a marginal cost curve visually represents the relationship between output and marginal cost. As production increases, one might expect that the marginal cost will initially decline due to the efficiencies gained from increased output. However, due to factors like diminishing returns, the marginal cost curve may eventually rise. Understanding this curve helps guide strategic decisions in resource allocation and can play an important role in cost minimization strategies.
The Role of Marginal Cost in Business Economics
In business economics, understanding marginal cost is essential for profit maximization. Evaluating how production costs vary with output enables firms to align their cost structure with pricing policies effectively. This careful alignment helps inform the decision-making process, allows for a more nuanced cost-benefit analysis, and affects overall market competition.
Marginal Cost and Marginal Revenue
The intertwined relationship of marginal cost and marginal revenue is critical for businesses. Understanding this relationship aids managers in identifying the output level that maximizes profits. If marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, increasing production should be the focus. Conversely, if marginal costs surpass marginal revenue, scaling back production can help in maintaining profitability levels, thus signifying the importance of constant monitoring and agile decision-making strategies.
Implications for Pricing Strategies
Determining the right pricing strategies involves understanding marginal cost pricing. By setting prices based on marginal cost ensures that consumers pay a fair price while covering production expenses. This principle also translates into cost leadership strategies and potential competitive advantages in saturated markets. Businesses that efficiently leverage marginal cost principles can achieve a sustainable edge over competitors.
Marginal Cost Examples in Business
Real-world applications of marginal cost can help clarify its significance. For instance, a bakery considering adding one more batch of cookies will find it beneficial to analyze the marginal cost, which includes extra ingredients, labor, and utility costs. If these costs are outweighed by the additional revenue generated from selling the cookies, the decision to produce more is justified. This straightforward example underlies the economic implications of evaluating production decisions based on informed marginal cost analyses.
Expanding Understanding of Marginal Cost
Gaining a deeper understanding of marginal cost allows businesses to navigate complex production scenarios. Improved proficiency in analyzing these costs can lead to better operational efficiencies and ideal resource allocation. Rearranging input costs based on marginal benefits transforms a static perspective into a dynamic one that aligns more closely with market realities.
Significance of Marginal Cost in Manufacturing
For manufacturers, marginal cost is a significant consideration as it directly impacts production costs and overall profitability. The ability to streamline processes and minimize marginal costs is closely linked to competitiveness. Efforts towards production optimization, understanding variable costs, and implementing efficient processes can lower production levels while maximizing output effectively.
Key Challenges in Marginal Cost Analysis
Businesses often face various challenges when conducting marginal cost assessments. Constraints like fluctuating raw material prices, changes in labor costs, and unexpected operational disruptions must all be taken into account. Recognizing these challenges enhances the ability to reevaluate the cost performance of operations and adapt strategies accordingly, thus contributing to overall financial health.
Real-World Marginal Cost Scenarios
Exploring marginal cost scenarios provides insight into practical challenges and viable solutions. Companies experiencing rapid growth might find that their current production capacity is reaching its limits. Evaluating marginal costs during periods of expansion can highlight when it’s economically viable to invest in new facilities or upgrade equipment. Such decisions can leverage economies of scale while simultaneously ensuring optimal production levels.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding marginal cost is vital for effective decision-making and cost management in business.
- The relationship between marginal cost and marginal revenue is critical for achieving profit maximization.
- In 2025, technology facilitates enhanced marginal cost calculations, leading to more informed production strategies.
- Real-world assessments and examples clarify how marginal cost can influence business economics.
- Understanding challenges and active adjustments to marginal cost approaches advance overall operational efficiency.
FAQ
1. What are the real-world applications of marginal cost?
Real-world applications of marginal cost include scenarios in manufacturing and retail where companies scale production. For example, a bakery using marginal cost analysis to determine the profitability of adding another batch of cookies can optimize output based on changing demand and cost structures. This allows firms to make better production decisions and pricing strategies based on real-time data.
2. How does marginal cost influence pricing strategies?
Marginal cost serves as a foundational element in determining pricing strategies. By understanding what it costs to produce one additional unit, businesses can set prices that not only ensure coverage of costs but also capture consumer willingness to pay. This method of pricing leads to efficient allocation of resources and maximizes potential profit margins in competitive markets.
3. What is the importance of understanding fixed costs vs marginal costs?
Differentiating between fixed costs and marginal costs is crucial for overall financial health. Fixed costs are incurred regardless of output, while marginal costs are directly tied to production changes. Understanding how these costs interact aids businesses in evaluating their spending, planning for scaling production, and striving for enhanced efficiency.
4. Can marginal cost change over time?
Yes, marginal costs can fluctuate due to a variety of factors, including changes in production methods, input costs, and operational efficiencies. External factors, such as market demand, supplier pricing, and competition, can also impact marginal costs, making it necessary for businesses to continuously evaluate and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
5. How do I include marginal cost in an economic model?
Incorporating marginal cost into an economic model involves using it as a variable when determining optimal production levels and pricing. Businesses should analyze past production data, current market conditions, and expected demand to integrate marginal cost in their models fully. This allows for precise financial forecasting and strategic decision-making.